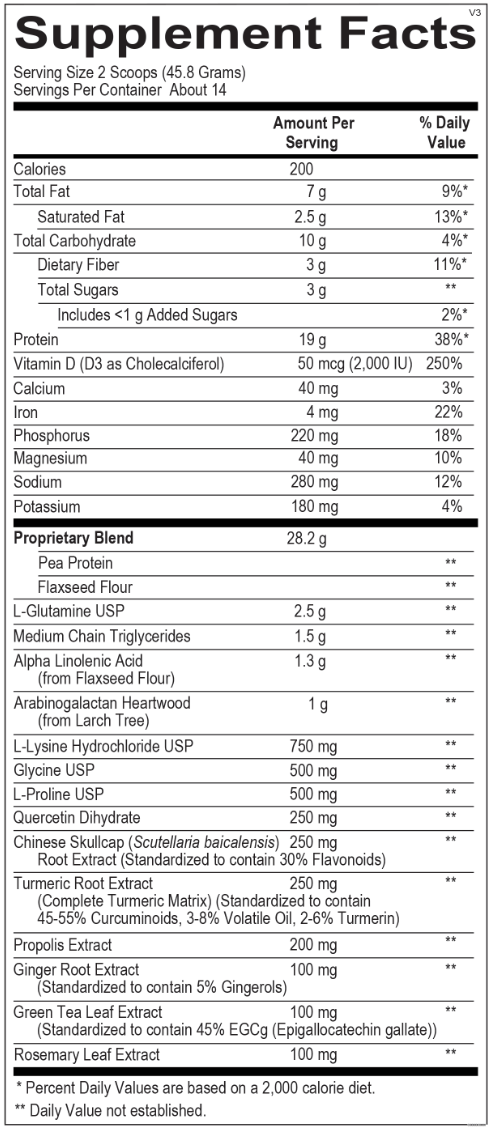
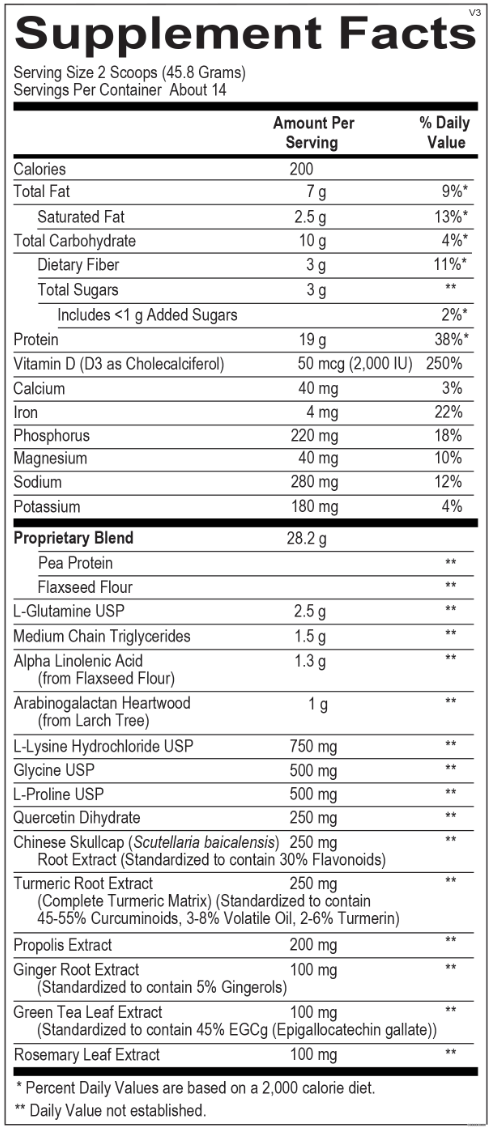
RSV Immunity | Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Immune Response
Ojus Life
| Explore the body's defense against RSV infection with insights into RSV immunity, highlighting the immune response mechanisms against Respiratory Syncytial Virus. |
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is one that causes infection in the lower respiratory tract, primarily during infancy and childhood. It is such a common virus that most children would have experienced its symptoms by the age of 2. However, it can also affect adults, where symptoms may mirror those of a common cold. It is noteworthy that symptoms can be severe in babies less than 12 months of age, older adults, or people who are already immunocompromised, which is why RSV immunity is essential.
Symptoms of Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Generally, symptoms of RSV start showing 4 to 6 days after the initial exposure to the virus. Older children and adults may experience common cold-like symptoms such as a dry cough, sore throat, headache, and a runny nose, among other things. However, in severe cases, the virus can spread to the lower respiratory tract and cause inflammation, leading to bronchiolitis or pneumonia. Symptoms of severe RSV may include a hoarse cough, high fever, wheezing, the skin turning slightly blue due to the lack of oxygen, and difficulty in breathing.
Once people are infected and build RSV immunity, it helps them recover within 2 weeks. However, in some cases, repeated wheezing might persist for a few more days. It is prudent to keep oneself isolated after experiencing any of the above symptoms as it is a highly contagious virus. This should be done at least until the patient develops RSV immunity after infection so that other people who come in contact are at a reduced risk.
Can you get RSV more than once?
RSV - like the common cold - can affect a person more than once. This is because RSV immunity after infection is not long-term; immunomodulation may be the cause as the virus could be interfering with the response. Studies show that RSV immunity duration is not too many months as reinfection is possible within the same year; albeit rare. Research also shows that RSV immunity after infection starts in 5 to 6 days; one can remain protected between 3 to 12 months. This is applicable to RSV immunity in adults, too.
How can you minimize an RSV infection or reinfection?
Respiratory viruses like a cough, cold, or RSV can be prevented in the same ways. They include:
- Cleaning your hands with soap or a sanitizer
- Covering your face with a mask when in public places
- Sanitizing frequently used objects like a laptop keyboard and smartphone
- Avoiding contact with people who have RSV
- Not sharing objects with people who have RSV
- Not putting your fingers in your eyes, nose, or mouth
Frequently Asked Questions
How long are you immune to RSV after having it?
RSV immunity in adults begins roughly 5 to 6 days after the first exposure to the virus. It can last from 3 to 12 months within a human system before it starts to gradually reduce, which is why one can get infected twice within a year.
How long after RSV exposure do symptoms occur?
Generally, signs and symptoms of an RSV infection start showing after 4 to 6 days after initial exposure to the virus. These include mild cough and cold-like symptoms such as a sore throat, fever, headache, a runny nose, and more.
How long does RSV stay in your system?
While mild cases of RSV can stay in your system for 1 to 2 weeks, more severe cases can extend up to a month. Even after recovery, certain patients with a severe infection can experience extended wheezing.
Can babies get RSV more than once?
Yes, babies can get RSV more than once, especially since their immune system has not developed completely. This is why it is imperative for adults to be careful when they have a cough or cold as if it is RSV, they can easily pass it on to their child.
While wearing masks was a mandate a couple of years ago, people have slowly started removing them and going back to routine life. The same goes for kids; they have started going back to school without masks. This is a reason that respiratory infections like RSV may be on the rise. Nobody is in danger as long as the infection is mild. However, when a severe infection causes the virus to reach the lower airways, that is when it becomes problematic and sometimes fatal.
It is prudent to take your child to the doctor if he or she shows even slight symptoms so that they can be put on treatment immediately; the same goes for adults. Patients who have a prevailing heart or lung ailment must take extra care.